Iliotibial (IT) Band Syndrome is a prevalent overuse injury that significantly impacts physical activity, particularly among runners and cyclists. The condition often causes burning in the knee, swelling, and pain along the lateral thigh and knee, stemming from friction between the iliotibial band and surrounding structures. Knowing the typical IT Band Syndrome recovery time and following proven treatments is essential for regaining mobility and preventing recurrence.
Individuals can recover successfully by addressing the root causes through physical therapy, tailored exercises, and at-home management strategies. This guide will provide insights into the causes, symptoms, and treatment of IT Band Syndrome while highlighting effective rehabilitation techniques.
What Is IT Band Syndrome?
Iliotibial Band Syndrome (ITBS) is one of the most prevalent injuries among runners and other long-distance athletes, yet the optimal management strategies for this condition remain an area of active exploration. Studies reveal that ITBS frequently affects individuals engaged in high-intensity athletic activities, such as long-distance running and cycling, emphasizing the need for targeted prevention strategies and rehabilitation programs.
Repetitive knee bending, particularly in activities like running or cycling, can irritate the IT bursa and surrounding tissues. This overuse often results in inflammation of the IT bursa, swelling, and discomfort. Left untreated, the condition may escalate, causing swelling and severe pain and hindering daily activities.
Causes and Risk Factors
IT Band Syndrome affects a wide range of individuals, not just runners. It is also common among military personnel undergoing intense physical training. For instance, more than 20% of U.S. Marines develop IT Band Syndrome during training programs. Additionally, the condition accounts for approximately 12% of all running-related injuries and is more prevalent in females than males. These statistics highlight the need to address gender-specific biomechanics and training practices to minimize the risk of IT Band Syndrome.
Common causes of IT Band Syndrome often stem from repetitive activities that strain the iliotibial band. Repetitive knee flexion, such as running or cycling, creates constant motion that irritates the band. Improper training techniques, like a sudden increase in exercise frequency or intensity, may also overload the IT band. Furthermore, poor biomechanics, including hip pulling inward, hip rotation weakness, and hip turning, contribute to uneven stress that exacerbates irritation.
Several risk factors increase susceptibility to IT Band Syndrome. Running on uneven surfaces can intensify friction and stress on the IT band. Preexisting iliotibial band tightness or a taut IT band makes individuals more vulnerable to irritation. Footwear and pronation issues, such as inadequate shoes or misaligned lower limbs, also play a role. Additionally, age reduces tissue elasticity, while muscle imbalances, particularly in the hip abductors or tensor fascia latae, further contribute to the development of this condition.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Timely identification and accurate diagnosis are critical for effective treatment. Early recognition of symptoms can prevent the condition from worsening and reduce the risk of prolonged recovery times. A comprehensive evaluation, including a discussion of exercise history and a physical examination, helps healthcare providers pinpoint the underlying causes and severity of the issue.
Identifying IT Band Syndrome Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms of IT Band Syndrome early is essential for effective treatment and recovery. The condition often begins with subtle signs that may be mistaken for general soreness or overuse but can progress to more debilitating pain if left unaddressed. Symptoms are usually linked to the iliotibial tract, a structure that plays a vital role in stabilizing the knee and hip during movement. Understanding the typical locations of pain, how symptoms evolve, and other associated indicators can help individuals seek timely medical intervention and prevent further complications. Below are key details to help identify the most common symptoms of IT Band Syndrome.
- Pain Location: Pain from IT Band Syndrome is commonly felt on the lateral side of the knee. In some cases, it may extend upward to the lateral part of the hip, indicating further irritation along the IT band.
- Progression of Symptoms: Early signs include discomfort during activity, which may worsen to redness and warmth around the knee or pain at rest.
- Associated Symptoms: Some individuals experience a clicking sensation or tenderness in the buttocks due to irritation of the iliotibial tract.
Diagnostic Procedures
Diagnosing IT Band Syndrome accurately is essential for effective treatment. Healthcare providers use a combination of physical exams, specialized tests, and imaging to confirm the condition and rule out similar issues like trochanteric bursitis. These methods help assess the severity and guide a personalized treatment plan.
- Physical Examination: A healthcare provider will assess the symptoms discussion, lower limbs assessment, and biomechanical abnormalities.
- Specialized Assessments: Tests like the Noble and Ober Test pinpoint tightness or irritation in the IT band. These assessments help healthcare providers accurately diagnose and develop targeted treatment plans.
- Imaging Tests: In severe cases, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or ultrasound may confirm a diagnosis or rule out other conditions like trochanteric bursitis or patellofemoral pain syndrome.
Recovery Time for IT Band Syndrome
The recovery timeline for IT Band Syndrome depends on several factors, including the severity and duration of the condition. Most patients undergoing conservative treatment methods, such as physical therapy, can return to running or their usual activities within six weeks. However, recovery following surgical interventions can extend to three months. Athletes are encouraged to gradually reintroduce activities to avoid persistent symptoms or the risk of new injuries, ensuring a safe and sustainable return to physical activity.
Typical Healing Duration
The recovery time for IT band syndrome varies based on the severity of the condition. Mild cases often improve within 4–6 weeks with proper care, while more severe cases may take several months. Adopting consistent rehabilitation and addressing individual factors can expedite recovery.
Factors Influencing Recovery
Recovery time for IT Band Syndrome depends on the severity of the injury, with advanced cases requiring longer healing. Early treatment, such as the RICE method, helps prevent complications, while adherence to rehabilitation protocols like stretching and strengthening exercises ensures optimal recovery.
- Severity of Injury: More advanced cases with significant inflammation of the IT bursa or associated conditions like greater trochanteric pain syndrome require longer recovery times.
- Prompt Treatment Initiation: Early diagnosis and conservative treatment, such as the RICE method (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation), can prevent complications.
- Adherence to Rehabilitation Protocols: Physical therapy for IT Band Syndrome, including stretching and strengthening, is essential for optimal recovery.
Physical Therapy for IT Band Syndrome
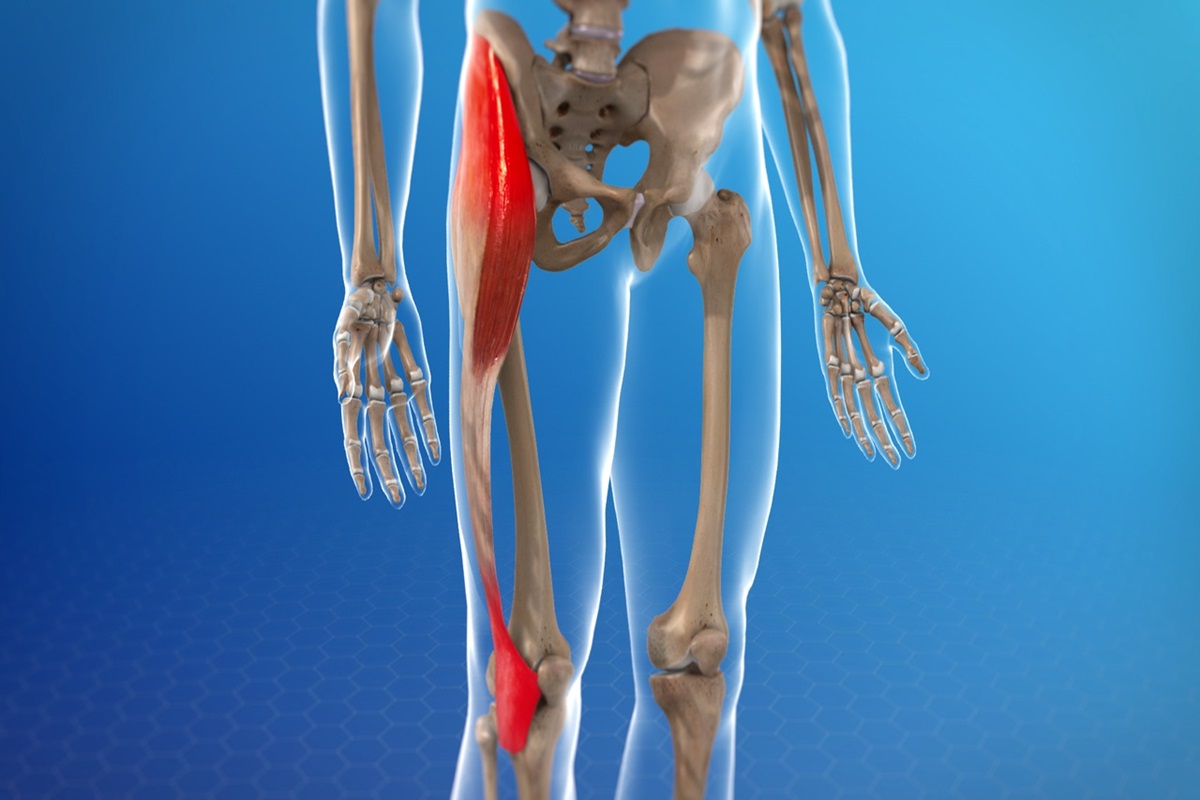
Physical therapy is a cornerstone of treatment for IT Band Syndrome, focusing on restoring function, relieving pain, and preventing recurrence. Physical therapy addresses underlying causes like muscle imbalances and iliotibial band tightness through stretching, strengthening, and mobility exercises. This approach ensures a comprehensive recovery and long-term resilience against future injuries.
At Austin Manual Therapy, we specialize in personalized care for musculoskeletal conditions like IT Band Syndrome, offering expert-guided solutions tailored to each individual. Our skilled therapists use evidence-based techniques to address the root causes of pain, improve mobility, and restore function. Whether seeking relief from persistent symptoms or a comprehensive rehabilitation plan, Austin Manual Therapy provides the professional care you need to recover effectively and prevent future injuries.
Role of Physical Therapy
IT Band Syndrome treatment often centers on physical therapy, which is crucial to recovery. Therapists focus on improving flexibility, strength, and biomechanics to alleviate pain and prevent recurrence. Incorporating graded strengthening exercises and mobility work ensures a balanced and effective rehabilitation approach tailored to the needs of each individual.
Physical Therapy Exercises for IT Band Syndrome
A targeted exercise program is essential for recovering from IT Band Syndrome. Stretching exercises like the standing stretch, foam roller stretch, and lying glute stretch help alleviate tension and improve flexibility in the IT band and surrounding tissues. Strengthening exercises, such as hip abductor strengthening, modified wall sit, and hip extension and rotation, correct muscle imbalances and improve stability. Additionally, foam rolling techniques reduce tightness in the iliotibial band and enhance overall recovery.
Stretching Exercises
Stretching exercises are a fundamental part of IT Band Syndrome recovery, as they help alleviate tension and improve flexibility in the affected areas. These stretches target the IT band and the surrounding muscles, which often contribute to tightness and discomfort. Incorporating these exercises into your routine can significantly enhance mobility and support overall recovery.
- Standing Stretch: This stretch helps lengthen the IT band and surrounding tissues, improving flexibility. It is especially useful for alleviating tightness in the lateral thigh.
- Foam Roller Stretch: Using a foam roller relieves tension in the IT band and promotes better circulation. Regular practice reduces stiffness and enhances recovery.
- Lying Glute Stretch: This stretch targets the tensor fascia latae and glutes, areas often associated with IT band tightness. It improves the range of motion and muscle balance.
Strengthening Exercises
Strengthening exercises are crucial for addressing the underlying muscle imbalances contributing to IT Band Syndrome. These exercises focus on building stability, particularly in the hips and glutes, which are critical in supporting proper movement mechanics. By targeting specific weaknesses, these exercises can help prevent recurrence and enhance overall physical performance.
- Hip Abductor Strengthening: These exercises address hip rotation weakness and enhance lateral stability. They play a key role in reducing strain on the IT band.
- Modified Wall Sit: This exercise builds endurance in the gluteal muscles, critical for maintaining proper alignment during activity. It also supports knee and hip stability.
- Hip Extension and Rotation: These movements improve stability and correct uneven muscle pull. They help create balance in the lower body, reducing the risk of IT band irritation.
Foam Rolling Techniques
- Proper foam rolling effectively reduces iliotibial band tightness and promotes flexibility. Incorporating this technique regularly aids in recovery and prevents stiffness. It also helps improve blood flow to the area, which supports faster healing. For best results, foam rolling should be done with controlled pressure and other rehabilitation exercises.
Additional Therapeutic Interventions
Additional therapies can complement physical rehabilitation for IT Band Syndrome. Manual therapy, including massage and foot mobilization techniques, helps reduce tightness and enhance alignment. Modalities like ultrasound and corticosteroid injections effectively manage pain and inflammation, supporting faster recovery.
- Manual Therapy: Techniques like massage and foot mobilization help reduce tightness in the IT band. They also improve alignment, promoting better movement and reducing discomfort.
- Modalities: Ultrasound and corticosteroid injections effectively manage pain and inflammation. These interventions support healing and complement other rehabilitation efforts.
Home Management Strategies
Effective home management is vital in supporting recovery from IT Band Syndrome. Simple yet impactful strategies like rest, icing, and activity modifications promote healing and reduce inflammation. Additionally, preventive measures such as proper warm-ups, cross-training, and choosing the right footwear help minimize the risk of future flare-ups.
At-Home Care
At-home strategies are crucial for managing IT Band Syndrome and supporting recovery. Rest and modifying physical activity allow the body’s natural healing processes to take effect while applying ice helps reduce inflammation and alleviate burning in the knee. Supportive insoles can improve alignment and minimize strain on the IT band, promoting better biomechanics.
- Rest and Modifying Physical Activity: Resting and avoiding the activity causing irritation allows the IT band to heal naturally. Reducing physical strain helps minimize further inflammation and discomfort.
- Application of Ice: Applying ice to the affected area helps reduce inflammation and ease burning in the knee. Regular icing also provides temporary pain relief during the recovery process.
- Supportive Insoles: Using supportive insoles can improve foot alignment and reduce strain on the IT band. Proper insoles also enhance overall comfort and prevent further biomechanical issues.
Preventive Measures
Preventing IT Band Syndrome involves proactive measures. A proper warm-up and cool-down routine prepares muscles and reduces the risk of injury while cross-training and improving running techniques prevent overuse. Additionally, changes to footwear that provide adequate support can significantly enhance biomechanics and lower the risk of recurrence.
- Proper Warm-Up and Cool-Down: A proper warm-up and cool-down routine is essential to prevent injury to the IT band. These practices prepare the muscles for activity and reduce post-exercise stiffness.
- Cross-Training and Running Technique Training: Incorporating diverse activities like swimming or cycling helps prevent overuse injuries. Refining your running technique can also improve biomechanics and reduce strain on the IT band.
- Changes to Footwear: Wearing supportive, well-fitted shoes is key to improving alignment and reducing stress on the IT band. Ensuring proper footwear also enhances comfort and prevents related injuries.
When to Seek Professional Help
While many cases of IT Band Syndrome improve with conservative care, some symptoms warrant professional intervention. Persistent pain, worsening inflammation, or frequent recurrence may indicate more severe underlying issues. Consulting a healthcare provider ensures accurate diagnosis and access to advanced treatment options if necessary.
Indications for Medical Consultation

It’s important to seek professional help if pain persists despite home therapy exercises or if symptoms such as swelling, severe pain, or hip pain worsen. Frequent recurrence of symptoms also indicates the need for a medical evaluation to address potential underlying issues. Consulting a healthcare provider ensures accurate diagnosis and access to advanced treatment options tailored to your condition.
Prognosis and Long-Term Management
With timely and consistent treatment, the prognosis for IT Band Syndrome is excellent. Most individuals fully recover and return to their regular activities without complications. Long-term management focuses on maintaining flexibility and strength through ongoing exercises, while periodic biomechanical assessments help prevent recurrence.
Expected Outcomes
With adherence to a treatment plan, most individuals experience a full recovery. Regular follow-ups ensure that the condition remains under control. Patients who prioritize consistent rehabilitation and make necessary adjustments to their activities often regain full mobility without recurring symptoms. Over time, maintaining proper biomechanics and strengthening exercises can further enhance long-term outcomes.
Maintenance Strategies
To prevent the recurrence of IT Band Syndrome and maintain long-term recovery, it’s essential to continue with graded strengthening exercises that target muscle imbalances and improve stability. Regularly reassessing biomechanics with a physical therapist ensures proper alignment and technique during physical activities, reducing the risk of future injuries and enhancing overall performance.
Conclusion
Overcoming IT Band Syndrome requires early intervention, a comprehensive rehabilitation plan, and a commitment to addressing underlying causes such as iliotibial band tightness, poor biomechanics, and muscle imbalances. By incorporating tailored physical therapy exercises for IT Band Syndrome, modifying physical activities, and consulting healthcare professionals for personalized treatment plans, individuals can achieve effective recovery and reduce the risk of recurrence. Whether through conservative methods like stretching, foam rolling, graded strengthening exercises, advanced treatments such as corticosteroid injections, or surgery for IT Band Syndrome, a proactive and consistent approach ensures long-term relief and a return to pain-free movement.
FAQs
Does IT Band Syndrome Ever Go Away?
Proper care can resolve the condition, including physical therapy exercises for IT Band Syndrome. However, maintaining preventive measures such as stretching and strengthening is crucial to avoid recurrence.
Does Physical Therapy Help IT Band Syndrome?
Absolutely. It addresses the root causes and restores mobility, improving outcomes. Physical therapy also helps correct biomechanical issues contributing to the condition, ensuring long-term relief.
What Is the Initial Treatment for IT Band Syndrome?
Conservative treatment methods like the RICE method, anti-inflammatory medications, and activity modification are the first line of defense. These approaches reduce inflammation and allow the affected tissues to begin healing naturally.